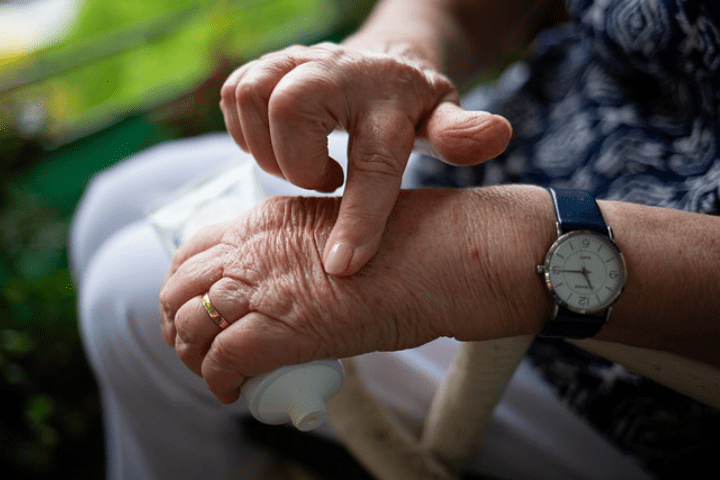

Arthritis is a catch-all term for around 200 conditions that inflame and damage joints. Nearly 1.5 million Americans are living with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in the joints. RA is the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, affecting women three times more often than men.
While the cause of RA is unknown, the disease occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints. This can lead to pain, swelling, stiffness and loss of movement in the affected joint.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary from person to person, and even from day to day. Some people experience a long period of remission, during which they may not have any symptoms. Others may have mild, intermittent symptoms for years before the disease becomes more severe.
The main symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are:
* joint pain and swelling
* stiffness, particularly in the morning
* a feeling of fatigue or tiredness
* loss of appetite
* weight loss
* depression or anxiety.
Rheumatoid Factor
Rheumatoid Factor is a substance that is produced by the body’s immune system and is found in the blood of people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Rheumatoid factor is an antibody that attacks the body’s own tissues. The presence of rheumatoid factor in the blood can be used to help diagnose RA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Causes
Many factors may be involved, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Some possible causes include:
-Autoimmune response: In people with rheumatoid arthritis, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. This may be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
-Infection: A bacterial or viral infection may trigger the autoimmune response that leads to rheumatoid arthritis.
-Hormonal changes: Changes in hormones such as estrogen and progesterone may contribute to the development of rheumatoid arthritis.
-Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.

Rheumatoid Arthritis Complications
There are many potential complications associated with rheumatoid arthritis. These can include:
* Joint deformity and destruction
* Stiffness in the joints
* Severe pain
* Reduced range of motion
* Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
* Thinning of the bones (osteoporosis)
* Heart problems
* Inability to use the hands and fingers
* Lung disease
Rheumatoid Arthritis Stages
There is no one definitive way to stage rheumatoid arthritis, as different clinicians may use different systems. However, a simplified way of staging RA is:
Early stage: Symptoms are mild and primarily involve the hands and feet.
Mild stage: Symptoms are more pronounced and may involve multiple joints throughout the body.
Moderate stage: The disease has progressed significantly and causes significant joint damage.
Severe stage: The disease has caused significant disability and joint damage, which may be accompanied by inflammation of other organs.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
A combination of medications, lifestyle changes and self-care may help control symptoms. Some common treatments for RA include:
· Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation and pain
· Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow or stop the progression of RA
· Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
· Physical therapy to improve joint function and mobility
· Occupational therapy to help with activities of daily living
· Pain relief medications such as acetaminophen or opioids
In addition to medication, there are a number of lifestyle changes that can help manage RA symptoms. These include:
· Exercising regularly – exercise can help keep joints flexible and improve overall health; aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity five days a week
· Maintaining a healthy weight – being overweight can put stress on joints and make them more painful; losing weight if needed can help ease symptoms
· Eating a healthy diet – omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oils may help reduce inflammation while fruits and vegetables provide important antioxidants; avoid processed foods and sugary drinks as they may aggravate symptoms
· Managing stress – stress can worsen inflammation and pain, so practices like yoga or meditation may be helpful in managing symptoms; seeking counseling or support groups may also be beneficial for some people with RA
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects the musculoskeletal system. RA is an autoimmune disease, meaning that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In RA, the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Over time, RA can damage the joints and other tissues in the body.
There is no cure for RA, but there are treatments that can help reduce inflammation and pain, and slow down the progression of the disease. Some common treatments for RA include medication such as anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and steroids; physical therapy; and surgery.
- A New Way of Looking at Arthritis: Healing Beyond the Joints|Joint Care TipsDiscover a transformative approach to arthritis. Learn how diet, movement, stress management, herbs, and lifestyle choices can reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and improve joint health naturally.… Read more: A New Way of Looking at Arthritis: Healing Beyond the Joints|Joint Care Tips
- Osteoarthritis Myths Debunked: Evidence-Based Truths About Joint Health: Joint Care TipsDebunking common osteoarthritis myths—discover the truth about joint regeneration, pain management, and non-surgical treatments. Learn how to protect your joints with science-backed strategies! Introduction Osteoarthritis (OA)… Read more: Osteoarthritis Myths Debunked: Evidence-Based Truths About Joint Health: Joint Care Tips
- How to Create a Daily Journal to Track Your Arthritis Symptoms: Joint Care TipsLearn how to create a simple and effective daily journal to track your arthritis symptoms, manage flare-ups, and improve your overall joint health. Introduction Arthritis can… Read more: How to Create a Daily Journal to Track Your Arthritis Symptoms: Joint Care Tips
- How to Use Natural Remedies to Enhance Your Arthritis Treatment Plan: Joint Care TipsDiscover natural remedies to complement your arthritis treatment plan. Learn about anti-inflammatory foods, herbal supplements, exercise, and lifestyle changes to reduce pain and improve joint health… Read more: How to Use Natural Remedies to Enhance Your Arthritis Treatment Plan: Joint Care Tips
- The Role of Vitamin D in Arthritis: Natural Sources and Benefits: Joint Care TipsDiscover the role of Vitamin D in arthritis, including its benefits for joint health, natural sources (sunlight, fatty fish, fortified foods), and how deficiency may worsen… Read more: The Role of Vitamin D in Arthritis: Natural Sources and Benefits: Joint Care Tips
Leave a comment